NURBS-Enhanced Finite Element Method for Hexahedral Meshes
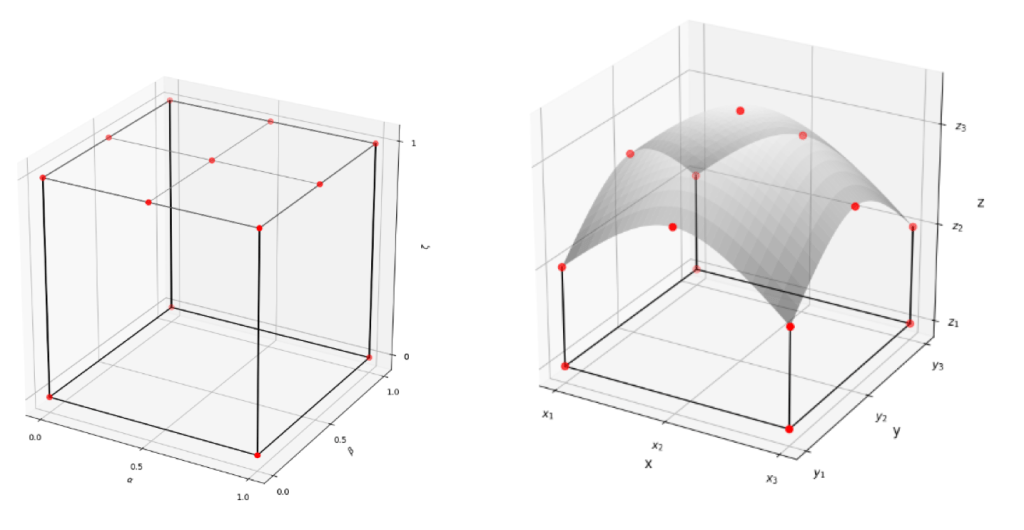
In this project, I introduce a NURBS-enhanced finite element method that integrates NURBS-based boundary representations of geometric domains into standard finite element frameworks applied to hexahedral meshes. I decompose an open, bounded, convex three-dimensional domain with a NURBS boundary into two parts, define the NURBS-enhanced finite elements over the boundary layer, and use piecewise-linear Lagrange finite elements in the interior region. I introduce a novel quadrature rule and a novel interpolation operator for the NURBS-enhanced elements. I also describe how the h-refinement in finite element analysis and the knot insertion in isogeometric analysis can be utilized in the refinement of the NURBS-enhanced elements. The proposed methodology combines the efficiency of finite element analysis with the geometric precision of NURBS, and may enable more accurate and efficient simulations over complex geometries.
Discrete Tensor-Product BGG Sequences: Splines and Finite Elements

We provide a systematic discretization of the Bernstein-Gelfand-Gelfand (BGG) diagrams and complexes over cubical meshes in arbitrary dimension via the use of tensor-product structures of one-dimensional piecewise-polynomial spaces, such as spline and finite element spaces. We demonstrate the construction of the Hessian, the elasticity, and div div complexes as examples for our construction.
A Multi‐Time Stepping Algorithm for the Modelling of Heterogeneous Structures With Explicit Time Integration

Heterogeneous solids often exhibit complex dynamic behavior, requiring simulations to use varying time steps. In this research, we propose a multi-time stepping algorithm that addresses this challenge by relaxing the constraint for an integer or constant time step ratio between subdomains and eliminating the need for kinematic interpolation. We propose an algorithm that ensures the satisfaction of the CFL condition and deviates only to allow subdomains to remain in synchronization. As a result, less integration steps are performed in comparison to state-of-the-art asynchronous integrators. We extend this algorithm to the coupling of multiple subdomains, where each subdomain has its own time step. Simulating stress wave propagation in meta-materials demonstrates that the proposed algorithm significantly accelerates simulation time, without sacrificing accuracy.
Macro Stokes elements

We construct a pair of conforming and inf-sup stable finite element spaces for the two– dimensional Stokes problem yielding divergence-free approximations on general convex quadrilateral partitions. The velocity and pressure spaces consist of piecewise quadratic and piecewise constant polynomials, respectively. We show that the discrete velocity and a locally post-processed pressure solution are second-order convergent.
Stokes elements on cubical meshes
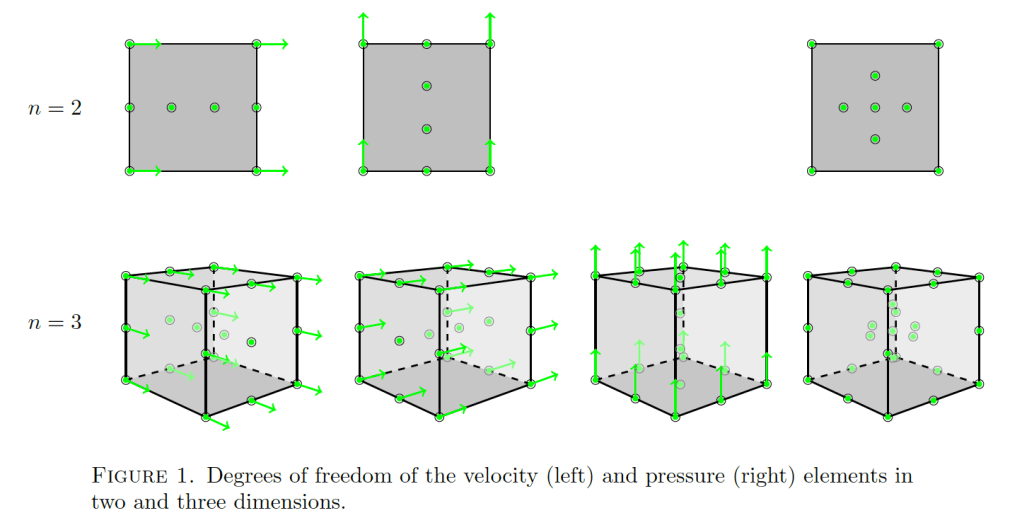
We construct conforming piecewise polynomial spaces with respect to cubic meshes for the Stokes problem in arbitrary dimensions yielding exactly divergence-free velocity approximations. The derivation of the finite element pair is motivated by a smooth de Rham complex that is well-suited for the Stokes problem. We derive the stability and convergence properties of the new elements as well as the construction of reduced elements with less global unknowns.
The Derivation of Dielectrical Breast Models for MRI Images for Breast Cancer Detection
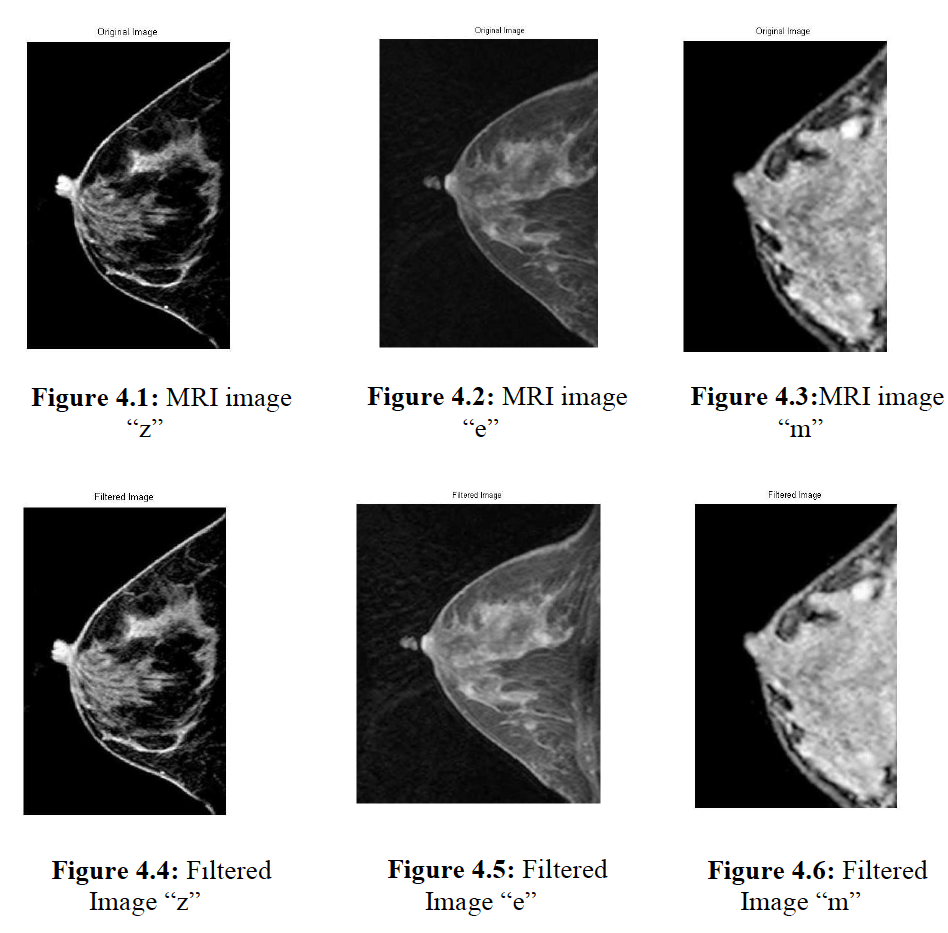
In this work, we investigate the electrical properties’ variations in breast tissues. We construct MRI-based breast models for use in the breast cancer research carried out at microwave frequencies. We utilize several image processing tools such as smoothing and edge detection filters, and Gaussian mixture models. We model the dielectric value distribution via piecewise-linear and cubic-spline interpolation techniques.
Genetic Algorithms Applied to Floor-plan Area Optimization Problem
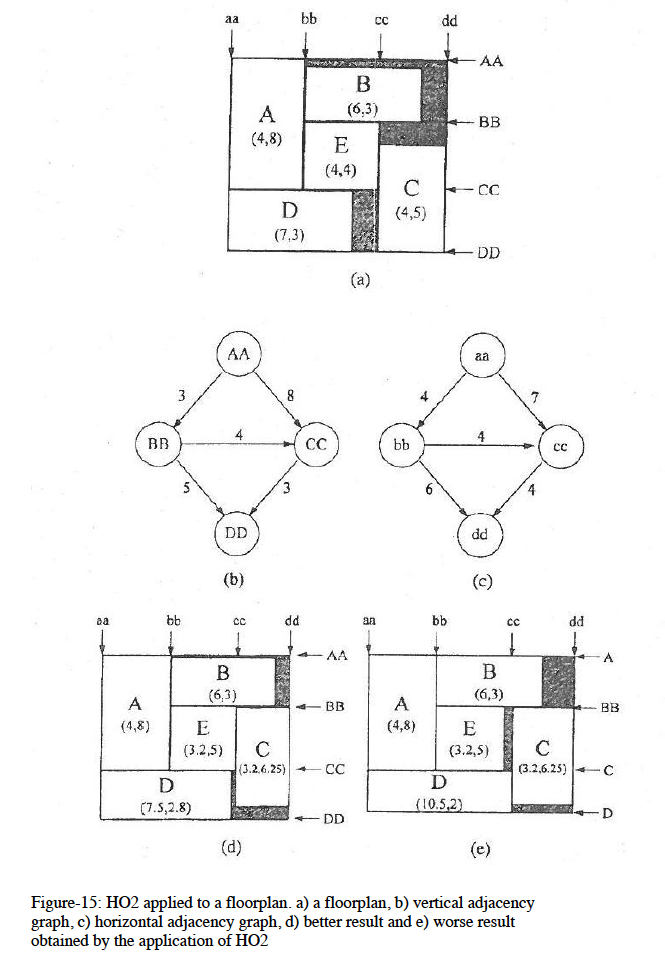
In this work, the representations of the floor-plan area designs are set forth with their effectiveness, a detailed analysis of the structure of genetic algorithms is made and the applications of genetic algorithms to the floor-plan area optimization problem are discussed comparatively.
Time Series Analysis Applied to Ionospheric Data
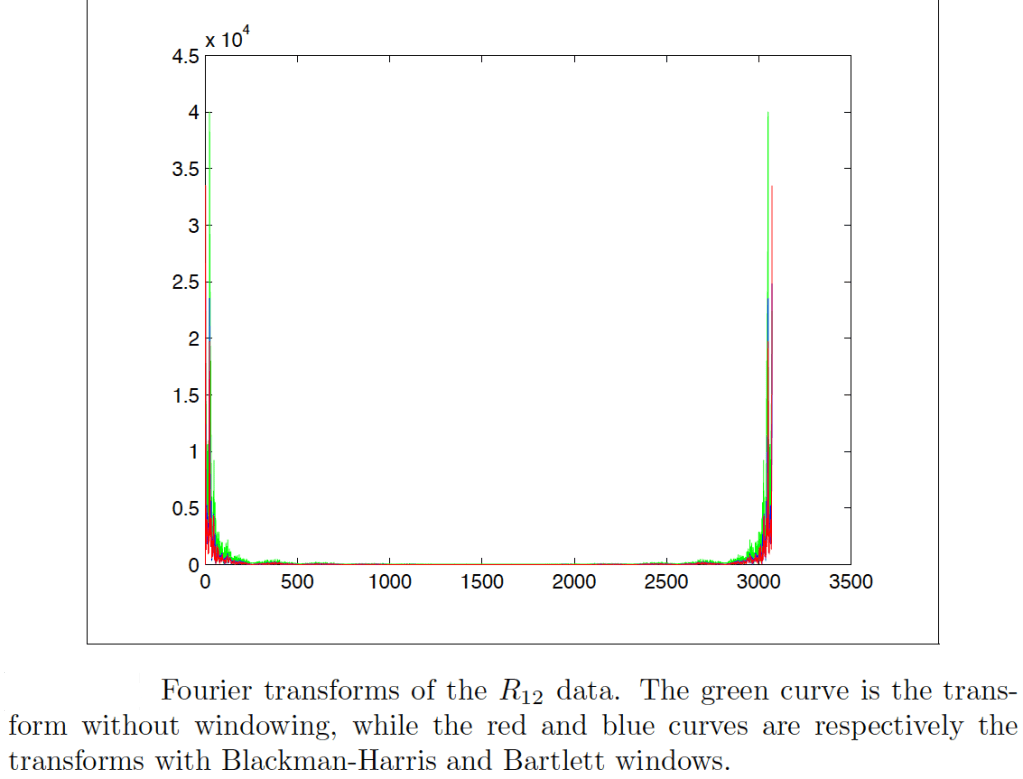
In this work, we use the source data provided by the Space Physics Interactive Data Resource (SPIDR). We build a regression model of the monthly-smoothed sunspot number data, R12, and search for the dominant periodicity for R12 using the sliding window technique.