Artificial Intelligence
Image Categorization and Search via a GAT Autoencoder and Representative Models
We present a method for comparing and categorizing images using graphs and graph attention networks (GATs). We first build a GAT-based autoencoder to derive representative models for a given set of image listings. Representative models capture the key features of each image by taking into account the similar images in its neighborhood. A GAT allows us to highlight important features and relationships between images. We construct a graph where nodes represent images (or their context-aware latent vectors) and edges capture similarity relationships, enabling us to categorize the representative models; thus, the image listings, into predefined categories. To categorize a new image, we extract its representative vector, compare it with the category representatives, identify the most likely category, and retrieve the most similar image within that category. We also present experimental results using both GAT autoencoders and standard feature-based techniques in our representative-centric approach.
Interoperability
Representation and System-Agnostic Automated CAD Interoperability Testing
In this project, we present theoretically-supported frameworks to test CAD system interoperability based on shape comparison criteria. We introduce a command line tool that provides indirect, representation-independent comparisons of CAD models via abstract proxies and query-based interpretations. Our frameworks support local comparisons using differential properties and offer a broad range of global comparisons. We allow testing for generic CAD software designed for different operating systems or scripting languages. Users can specify tolerance values for testing, ensuring accuracy. This approach bridges CAD model representations, enabling effective interoperability evaluation across diverse systems without requiring in-depth knowledge of CAD software or representations.
On Verification of Interoperability of CAD Systems with a Focus on Invariant Properties
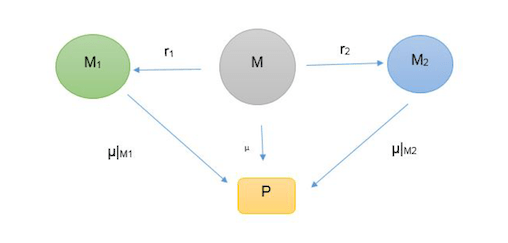
Interoperability is the ability of a system to correctly interpret and function with another system’s components and products. In this paper, we propose a theoretical framework for the verification of (geometric) interoperability that would allow distinct CAD systems to interact with each other through a query-based data acquisition and exchange. In this regard, we establish a correspondence based on a topological equivalence and a geometric similarity between model instances authored by distinct systems.
An Automated Approach for the Discovery of Interoperability
In this article, we present an automated approach that would test for and discover CAD-to-CAD interoperability based on the approximately-invariant shape properties between two given CAD models. We further show that exchanging models in standard format does not guarantee the preservation of shape properties. We generate template files to accommodate the information necessary for the property computations and proxy model constructions, and implement an interoperability discovery program called DTest to execute the interoperability testing.
Geometry Validation
A Review of Geometric Integrity Criteria for Military Standards – 31000A
In this article, we focus on the geometric integrity criteria presented in MIL-STD 31000A. We present a general review of the geometric integrity criteria and recommend a method that focuses on the investigation of geometric and topological property violations to identify defects. We propose ways to improve the geometric integrity criteria classes and the recommended correction methods provided. We point out how the categorization of the tests based on dimensionality arguments or experimental observations creates repetition in testing.
